
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of EMW Information (MoE), Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China
2 Department of Communication Science and Engineering, Shanghai ERC of LEO Satellite Communication and Applications, Shanghai CIC of LEO Satellite Communication Technology, Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China
3 Department of Electronic Engineering, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
4 School of Information and Electronics, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
Increasing bandwidth requirements have posed significant challenges for traditional access networks. It is difficult for intensity modulation/direct detection to meet the power budget and flexibility requirements of the next-generation passive optical network (PON) at 100G and beyond considering the new requirements. This is driving researchers to develop novel optical access technologies. Low-cost, wide-coverage, and high-flexibility coherent PON is emerging as a strong contender in the competition. In this article, we will review technologies that reduce the complexity of coherent PON (CPON), enabling it to meet the commercial requirements. Also, advanced algorithms and architectures that can enhance system coverage and flexibility are also discussed.
access network coherent optics flexible data rate low complexity wide dynamic range Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(4): 040604

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of EMW Information (MoE), Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China
2 Shanghai ERC of LEO Satellite Communication and Applications, Shanghai CIC of LEO Satellite Communication Technology, Shanghai 200433, China
3 Science and Technology on Electromagnetic Compatibility Laboratory, China Ship Development and Design Centre, Wuhan 430000, China
4 Peng Cheng Laboratory, Shenzhen 518055, China
This paper experimentally demonstrates a distributed photonics-based W-band integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) system, in which radar sensing can aid the communication links in alignment and data rate estimation. As a proof-of-concept, the ISAC system locates the users, guides the alignment, and sets a communication link with the estimated highest data rate. A peak net data rate of 68.6 Gbit/s and a target sensing with a less-than-1-cm error and a sub-2-cm resolution have been tested over a 10-km fiber and a 1.15-m free space transmission in the photonics-based W-band ISAC system. The achievable net data rates of the users at different locations estimated by sensing are experimentally verified.
integrated sensing and communication photonics-aided technique W-band radar-aided flexible communication Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(4): 043901
复旦大学信息科学与工程学院电磁波信息科学教育部重点实验室,上海 200433
为了在保持帧结构完整性的同时,低代价地传输管理和控制信号,提出面向高速频分复用相干无源光网络(FDM-CPON)的两种传输管理和控制信号传输机制,即数字端辅助管理和控制通道(AMCC)和数据通道的相加和相乘。通过将AMCC传输的通断键控(OOK)信号映射为数据通道信号幅值的变化,完成数据通道信号幅值再调制,成功将AMCC与数据通道相结合,实现了管理和控制信号与数据通道信号的同步传输。实验结果表明,在基于16QAM传输20 km光纤的200 Gbit/s FDM-CPON系统中,当AMCC的带宽和调制因子(MI)相同时,乘性AMCC对于信号性能的影响更小,自身传输信号的质量也更高。在AMCC的MI为26.1%、带宽为24.4 MHz时,乘性AMCC对信号灵敏度的惩罚比加性AMCC小3 dB。以上研究为未来高速相干频分复用无源光网络AMCC传输与系统设计提供重要参考。
光通信 相干无源光网络 相干光通信 光纤通信 频分复用 辅助管理和控制通道
光通信研究
2024, 50(1): 23014301

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory for Information Science of Electromagnetic Waves (MoE), Department of Communication Science and Engineering, Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China
2 National Institute of LED on Silicon Substrate, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330096, China
In recent studies, visible light communication (VLC) has been predicted to be a prospective technique in the future 6G communication systems. To suit the trend of exponentially growing connectivity, researchers have intensively studied techniques that enable multiple access (MA) in VLC systems, such as the MIMO system based on LED devices to support potential applications in the Internet of Things (IoT) or edge computing in the next-generation access network. However, their transmission rate is limited due to the intrinsic bandwidth of LED. Unfortunately, the majority of visible light laser communication (VLLC) research with beyond 10 Gb/s data rates concentrates on point-to-point links, or using discrete photodetector (PD) devices instead of an integrated array PD. In this paper, we demonstrated an integrated PD array device fabricated with a Si-substrated GaN/InGaN multiple-quantum-well (MQW) structure, which has a array of micro-PD units with a common cathode and anode. This single-integrated array successfully provides access for two different transmitters simultaneously in the experiment, implementing a MIMO-VLLC link at 405 nm. The highest data rate achieved is 13.2 Gb/s, and the corresponding net data rate (NDR) achieved is 12.27 Gb/s after deducing the FEC overhead, using 2.2 GHz bandwidth and superposed PAM signals. Furthermore, we assess the Huffman-coded coding scheme, which brings a fine-grain adjustment in access capacity and enhances the overall data throughput when the user signal power varies drastically due to distance, weather, or other challenges in the channel condition. As far as we know, this is the first demonstration of multiple visible light laser source access based on a single integrated GaN/InGaN receiver module.
Photonics Research
2024, 12(4): 793

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory for Information Science of Electromagnetic Waves (MoE), Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China
2 Peng Cheng Laboratory, Shenzhen 518038, China
In this Letter, we propose and experimentally demonstrate a lens-free wavefront shaping method that utilizes synchronized signal block beam alignment and a genetic algorithm (SSBGA) for a diffuse non-line-of-sight (NLOS) visible light communication (VLC) system. The proposed method effectively controls the position and mobility of visible light beams by partitioning spatial light modulator pixels and manipulating beams to converge at distinct spatial positions, thereby enhancing wavefront shaping efficiency, which achieves a significant 23.9 dB optical power enhancement at offset, surpassing the lens-based continuous sequence (CS) scheme by 21.7 dB. At angle, the improvement reaches up to 11.8 dB and 16.8 dB compared to the results with and without lens-based CS, respectively. A maximum rate of 5.16 Gbps is successfully achieved using bit-power loading discrete multi-tone (DMT) modulation and the proposed SSBGA in an NLOS VLC system, which outperforms the lens-based CS by 1.07 Gbps and obtains a power saving of 55.6% during the transmission at 4 Gbps. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time that high-speed communication has been realized in an NLOS VLC system without a lens.
non-line-of-sight, lens-free wavefront shaping visible light communication Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(2): 020603
Author Affiliations
Abstract
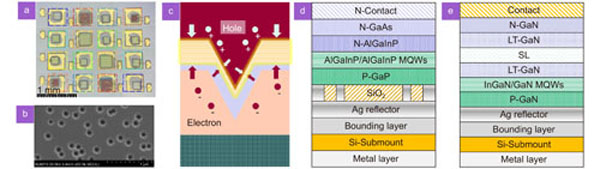
Although the 5G wireless network has made significant advances, it is not enough to accommodate the rapidly rising requirement for broader bandwidth in post-5G and 6G eras. As a result, emerging technologies in higher frequencies including visible light communication (VLC), are becoming a hot topic. In particular, LED-based VLC is foreseen as a key enabler for achieving data rates at the Tb/s level in indoor scenarios using multi-color LED arrays with wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) technology. This paper proposes an optimized multi-color LED array chip for high-speed VLC systems. Its long-wavelength GaN-based LED units are remarkably enhanced by V-pit structure in their efficiency, especially in the “yellow gap” region, and it achieves significant improvement in data rate compared with earlier research. This work investigates the V-pit structure and tries to provide insight by introducing a new equivalent circuit model, which provides an explanation of the simulation and experiment results. In the final test using a laboratory communication system, the data rates of eight channels from short to long wavelength are 3.91 Gb/s, 3.77 Gb/s, 3.67 Gb/s, 4.40 Gb/s, 3.78 Gb/s, 3.18 Gb/s, 4.31 Gb/s, and 4.35 Gb/s (31.38 Gb/s in total), with advanced digital signal processing (DSP) techniques including digital equalization technique and bit-power loading discrete multitone (DMT) modulation format.
GaN-based LED LED array VLC V-pit sidewall quantum well high-frequency response Opto-Electronic Science
2023, 2(5): 230005
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory for Information Science of Electromagnetic Waves (MoE), Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China
2 Shanghai Engineering Research Center of Low-Earth-Orbit Satellite Communication and Applications, Shanghai 200433, China
3 Shanghai Collaborative Innovation Center of Low-Earth-Orbit Satellite Communication Technology, Shanghai 200433, China
4 National Institute of LED on Silicon Substrate, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330096, China
5 Peng Cheng Laboratory, Shenzhen 518055, China
6 e-mail:
7 e-mail:
8 e-mail:
Visible light communication (VLC) has emerged as a promising communication method in 6G. However, the development of receiving devices is much slower than that of transmitting devices, limited by materials, structures, and fabrication. In this paper, we propose and fabricate an InGaN/GaN multiple-quantum-well-based vertical-structure micro-LED-based photodetector (μPD) on a Si substrate. A comprehensive comparison of the photoelectrical performance and communication performance of three sizes of μPDs, 10, 50, and 100 μm, is presented. The peak responsivity of all three μPDs is achieved at 400 nm, while the passband full-widths at half maxima are 87, 72, and 78 nm for 10, 50, and 100 μm μPDs, respectively. The cutoff bandwidth is up to 822 MHz for 50 μm μPD. A data rate of 10.14 Gbps is experimentally demonstrated by bit and power loading discrete multitone modulation and the proposed digital pre-equalizer algorithm over 1 m free space utilizing the self-designed 50 μm μPD array as a receiver and a 450 nm laser diode as a transmitter. This is the first time a more than 10 Gbps VLC system has been achieved utilizing a GaN-based micro-PD, to the best of our knowledge. The investigation fully demonstrates the superiority of Si substrates and vertical structures in InGaN/GaN μPDs and shows its great potential for high-speed VLC links beyond 10 Gbps.
Photonics Research
2022, 10(10): 2394

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Optical Communication Technologies and Networks, China Information and Communication Technologies Group Corporation (CICT), Wuhan 430074, China
2 National Information Optoelectronics Innovation Center, Wuhan 430074, China
3 Key Laboratory of Information Science of Electromagnetic Waves (MoE), Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China
4 Peng Cheng Laboratory, Shenzhen 518055, China
An ultrafast microring modulator (MRM) is fabricated and presented with of . A 240 Gb/s PAM-8 signal transmission over 2 km standard single-mode fiber (SSMF) is experimentally demonstrated. PN junction doping concentration is optimized, and the overall performance of the MRM is improved. Optical peaking is introduced to further extend the EO bandwidth from 52 to 110 GHz by detuning the input wavelength. A titanium nitride heater with 0.1 nm/mW tuning efficiency is implemented above the MRM to adjust the resonant wavelength. High bit rate modulations based on the high-performance and compact MRM are carried out. By adopting off-line signal processing in the transmitter and receiver side, 120 Gb/s NRZ, 220 Gb/s PAM-4, and 240 Gb/s PAM-8 are measured with the back-to-back bit error ratio (BER) of , , and , respectively. A BER with different received optical power and 2 km SSMF transmission is also investigated. The BER for 220 Gb/s PAM-4 and 240 Gb/s PAM-8 after 2 km SSMF transmission is calculated to be and , which meet with the threshold of soft-decision forward-error correction, respectively.
Photonics Research
2022, 10(4): 04001127
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory for Information Science of Electromagnetic Waves (MoE), Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, People’s Republic of China
2 National Institute of LED on Silicon Substrate, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330096, People’s Republic of China
3 State Key Laboratory of Precision Spectroscopy, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200241, People’s Republic of China
4 State Key Laboratory of Optical Communication Technologies and Networks, China Information Communication Technologies Group Corporation, Wuhan 430000, People’s Republic of China
5 Peng Cheng Laboratory, Shenzhen, 518055, China
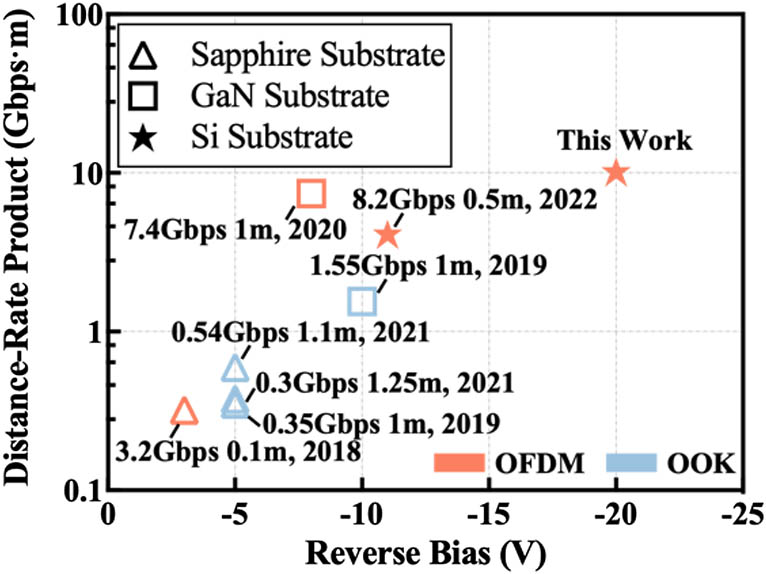
High-speed visible light communication (VLC), as a cutting-edge supplementary solution in 6G to traditional radio-frequency communication, is expected to address the tension between continuously increased demand of capacity and currently limited supply of radio-frequency spectrum resource. The main driver behind the high-speed VLC is the presence of light emitting diode (LED) which not only offers energy-efficient lighting, but also provides a cost-efficient alternative to the VLC transmitter with superior modulation potential. Particularly, the InGaN/GaN LED grown on Si substrate is a promising VLC transmitter to simultaneously realize effective communication and illumination by virtue of beyond 10-Gbps communication capacity and Watt-level output optical power. In previous parameter optimization of Si-substrate LED, the superlattice interlayer (SL), especially its period number, is reported to be the key factor to improve the lighting performance by enhancing the wall-plug efficiency, but few efforts were made to investigate the influence of SLs on VLC performance. Therefore, to optimize the VLC performance of Si-substrate LEDs, we for the first time investigated the impact of the SL period number on VLC system through experiments and theoretical derivation. The results show that more SL period number is related to higher signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) via improving the wall-plug efficiency. In addition, by using Levin-Campello bit and power loading technology, we achieved a record-breaking data rate of 3.37 Gbps over 1.2-m free-space VLC link under given optimal SL period number, which, to the best of our knowledge, is the highest data rate for a Si-substrate LED-based VLC system.





